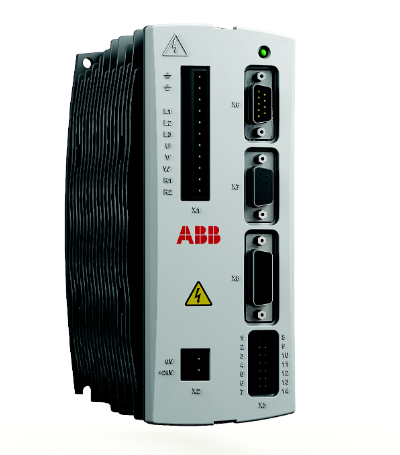
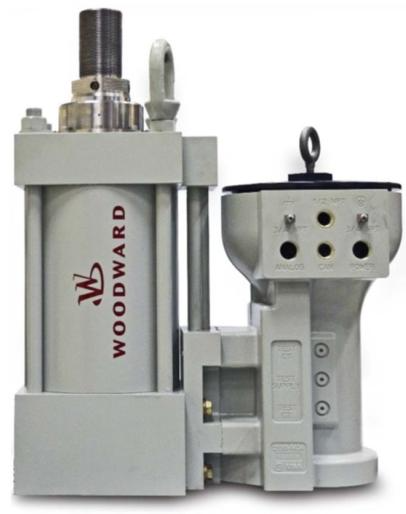
XO16N1-B20 and XO16N1-C3.0 are both high-performance industrial control modules under the ABB AC 500 eco series, focusing on signal acquisition and logic control for small and medium-sized industrial control systems. Their core function is to receive on-site sensor signals, execute preset control programs, and issue instructions to actuators. They are widely applicable to scenarios such as automated production lines, intelligent buildings, and small and medium-sized water treatment equipment, especially for applications that require high control response speed and module cost-effectiveness.
ABB XO16N1-B20 XO16N1-C3.0 High-Performance Industrial Control Module
Product positioning and core values
XO16N1-B20 and XO16N1-C3.0 are both high-performance industrial control modules under the ABB AC 500 eco series, focusing on signal acquisition and logic control for small and medium-sized industrial control systems. Their core function is to receive on-site sensor signals, execute preset control programs, and issue instructions to actuators. They are widely applicable to scenarios such as automated production lines, intelligent buildings, and small and medium-sized water treatment equipment, especially for applications that require high control response speed and module cost-effectiveness.
The core values of both are unified as "high response+flexible adaptation+high cost-effectiveness": using high-speed signal processing chips, control command response time ≤ 1ms; supporting compatibility with ABB's full range of I/O modules, terminal units, and third-party devices, and can expand system scale as needed; Modular design reduces initial investment costs while simplifying later maintenance processes, balancing performance and economic requirements.
Core parameters and functional differences (B20 vs C3.0)
1. Common parameters (consistent basic performance)
Processor configuration
32-bit single core processor, clock speed 800MHz, memory capacity 512MB DDR3 (program storage)+2GB eMMC (data storage), supports online program modification
Programming support
Compatible with ABB Control Builder Plus software (version ≥ 5.1), supporting ladder diagram (LD), functional block diagram (FBD), and structured text (ST) programming
Communication interface
2 100Mbps Ethernet ports (supporting Modbus TCP, EtherNet/IP protocols), 1 RS485 serial port (supporting Modbus RTU protocol), 1 USB 2.0 interface (program download/data backup)
Power parameters
24V DC power supply (input range 18-30V DC), power consumption ≤ 8W, with overvoltage and overcurrent protection (protection thresholds are 36V DC and 2A, respectively)
Environmental adaptability
Working temperature -20 ℃ to 60 ℃, relative humidity 5% -95% (non condensing), protection level IP20 (module body), anti vibration performance 10-500Hz, 0.05g
2. Core differences (different functional emphasis)
Comparing dimensions
XO16N1-B20 (logic control type)
XO16N1-C3.0 (Process Control Type)
Focus on control functions
Main digital logic control, supporting 16 digital input (DI)+16 digital output (DO), DO output type is relay contact (2A/250V AC), suitable for switch actuators such as contactors and solenoid valves
Focusing on analog process control, supporting 8 analog inputs (AI, 4-20mA/0-10V)+8 analog outputs (AO, 4-20mA), AI sampling accuracy ± 0.1%, suitable for regulating devices such as sensors and frequency converters
Special feature support
Built in 16 timers/counters (timing range 1ms-1000h, counting range 0-65535), supporting pulse capture (capture frequency ≤ 1kHz)
Supports 8 PID control loops (PID parameters can be tuned online), with analog signal filtering (filter coefficient 1-100 adjustable), suitable for continuous adjustment scenarios such as temperature and pressure
Expansion capability
Supports up to 4 I/O modules for expansion (such as DI801 digital input module), only compatible with digital expansion units
Supports up to 6 I/O modules expansion (such as AI801 analog input module, AO801 analog output module), compatible with mixed analog/digital expansion
Typical application scenarios
Motor start stop control, conveyor logic interlocking, and equipment status monitoring (such as button and travel switch signal acquisition) for automated production lines
PH regulation, temperature control of constant temperature water tank, and pressure stabilization of pressure tank in small and medium-sized water treatment plants (such as sensor signal acquisition+frequency converter speed adjustment)
Adaptation devices and collaborative applications
1. Core adaptation devices (universal and differential adaptation for both)
Adapt to device types
Universal adaptation (supported by B20/C3.0)
XO16N1-B20 exclusive adaptation
XO16N1-C3.0 exclusive adaptation
Terminal unit
ABB TU515 I/O terminal unit (connected via TK516 cable for signal transfer)
Connecting cables
TK516 with contact connection cable (I/O module terminal unit), CAT5e 100Mbps Ethernet cable (communication connection)
Power module
ABB PM510 power module (24V DC/1A output, supplying power to the module and expansion unit)
External actuator
AC contactors (such as ABB AX series, 220V AC coils), solenoid valves (24V DC)
Inverter (such as ABB ACS150 series), regulating valve (4-20mA control signal)
External sensors
Travel switch (such as ABB LS series, 24V DC), photoelectric sensor (NPN output)
PT100 temperature sensor (4-20mA transmission output), pressure sensor (0-10V signal)
Expand I/O module
DI801 digital input module (32 DI channels), DO801 digital output module (32 DO channels)
AI801 analog input module (16 channels AI), AO801 analog output module (16 channels AO)
2. Collaborative application cases with TU515 and TK516
Case 1: XO16N1-B20+TU515+Production Line Motor Control
The stroke switch signals (DI) of three motors on the production line are connected to the TU515 terminal unit (1-3 sets of terminals), and the TU515 is connected to the DI interface of XO16N1-B20 through TK516 cable; The DO interface of XO16N1-B20 is connected to TU515 (4-6 terminals) through another set of TK516 cables, and TU515 outputs a 24V DC signal to control the motor contactor coil. When the travel switch is triggered, XO16N1-B20 executes the logic program to achieve the chain control of "motor 1 starts → delayed 2s starts motor 2 → delayed 3s starts motor 3", with a response time of ≤ 500ms, avoiding grid impact caused by simultaneous motor starts.
Case 2: XO16N1-C3.0+TU515+Constant Temperature Water Tank Control
The PT100 temperature sensor (4-20mA signal) of the water tank is connected to the TU515 terminal unit (1 set of terminals) and transmitted to the AI interface of XO16N1-C3.0 through TK516 cable; XO16N1-C3.0 runs the PID program, and based on the deviation between the measured temperature and the set value (such as 50 ℃), outputs a 4-20mA signal through the AO interface (via TU515 relay) to control the speed of the heating rod inverter. The AI sampling accuracy is ± 0.1%, and the temperature fluctuation after PID regulation is stable is ≤ ± 0.3 ℃, meeting the requirements of precision temperature control.
Installation and programming specifications
1. Installation process (both consistent, simplified version)
Rail fixation: Insert the module along the 35mm DIN rail, rotate it 90 ° and clamp it tightly. The distance between adjacent devices (such as power modules and expansion I/O modules) should be ≥ 5mm to ensure heat dissipation; The module grounding terminal ("PE") is connected to the cabinet grounding strip, with a grounding resistance of ≤ 1 Ω.
Power connection: Use a 1.5mm ² copper wire to connect the "+24V" and "GND" terminals of the PM510 power module to the module power input terminal, paying attention to polarity (reverse connection will trigger overcurrent protection and lock the module).
Signal connection: The TU515 terminal unit is connected to the module I/O interface (DI/DO or AI/AO) through a TK516 cable. When inserting the cable, it needs to be aligned with the guide slot (locked upon hearing a "click" sound); Ethernet port 1 is connected to the upper monitoring computer (for debugging purposes), and Ethernet port 2 is connected to the industrial switch (for networking purposes).
2. Programming and debugging points (differential adaptation)
XO16N1-B20 (Logic Control):
Create a 'Logic Control Project' using Control Builder Plus and implement timer/counter functions (such as motor start delay) through FBD programming; During debugging, first verify the DO output logic by forcing the DI signal (such as forcing the travel switch signal and observing whether the contactor is in operation), and then connect it to the on-site equipment for linkage testing to avoid misoperation.
XO16N1-C3.0 (Process Control):
Create a "process control project" and configure the AI/AO signal range in the software (e.g. AI channel 1 is set to 4-20mA corresponding to 0-100 ℃); Initial setting of PID loop parameters: proportional coefficient (P)=5, integration time (I)=10s, differentiation time (D)=1s. Optimize parameters through online monitoring of the "deviation curve" (increase P if temperature fluctuations are large, decrease I if response is slow).

- User name Member Level Quantity Specification Purchase Date
- Satisfaction :
-