Allen Bradley 1336 PLUS II Adjustable Frequency Driver
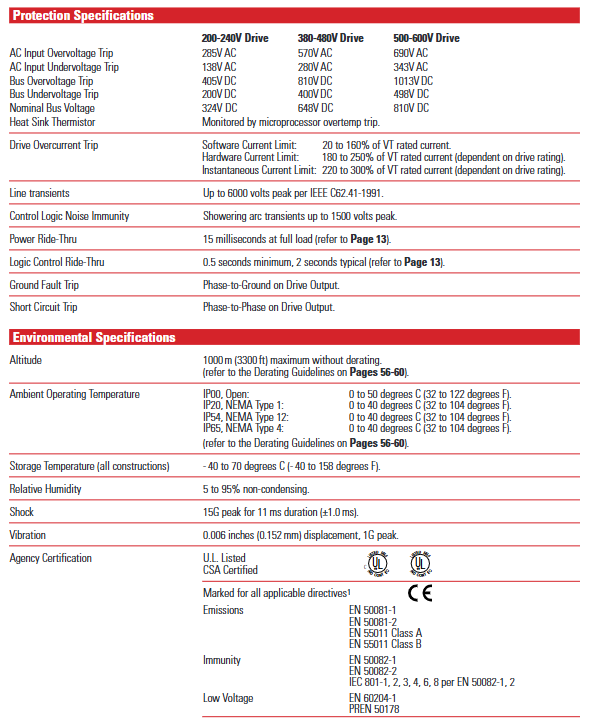
Power outage response: Supports two modes of "line loss fault enable/disable". When there is a line loss, the operation is maintained through DC bus energy storage. When the bus voltage drops to 85% of the rated value, the output is turned off. After power is restored, it can be restarted through methods such as flying start and detecting motor voltage.
3. Monitoring and Diagnosis
Real time monitoring: Display output current, voltage, frequency, temperature and other parameters through HIM's backlight ultra twisted LCD (2 lines x 16 characters), supporting multilingual switching; The "Process Display" mode allows customization of display units and parameter combinations (such as "121.6 In/min" and "2.7AmPs").
Fault recording and diagnosis: Cache the last 4 faults and automatically start the fault diagnosis program upon startup; When there is a malfunction, display a prompt in _plain language_ (such as "Undervolt Fault" or "Overtemp Fault") and report the status through the HIM or SCANPort communication port.
Installation and Wiring Guide
1. Installation requirements
Size and weight: There are significant differences in the size of drivers with different frames (A1-G). Taking IP20 (NEMA Type 1) as an example, A1 frame size is 215.9 × 290.0 × 160.0mm (width × height × depth), weighing 4.31kg; G frame size is 635.0 × 2324.1 × 508.3mm, weighing 453.6kg (please refer to the specific frame size table).
Installation spacing: At least 152.4mm (6 inches) of ventilation space should be reserved on both sides and the back; The F-frame drive requires additional side/back space, and when the open drive is installed in the user housing, it needs to be equipped with two 725 CFM fans (BPR series requires fans of 450 CFM or above).
2. Wiring specifications
Power wiring (TB1 terminal): input terminals R (L1), S (L2), T (L3), output terminals U (T1), V (T2), W (T3), DC bus terminal+DC/- DC, grounding terminals PE (protective ground), TE (shielding ground); 75 ℃ copper wire is required, with different wire diameters for different frame terminals (maximum 5.3mm ²/10AWG for A1-A4 frame, maximum 303.6mm ²/600MCM for G frame), and torque must comply with specifications (such as 1.81N/m/16lb in for A1-A4 frame).
Control and signal wiring:
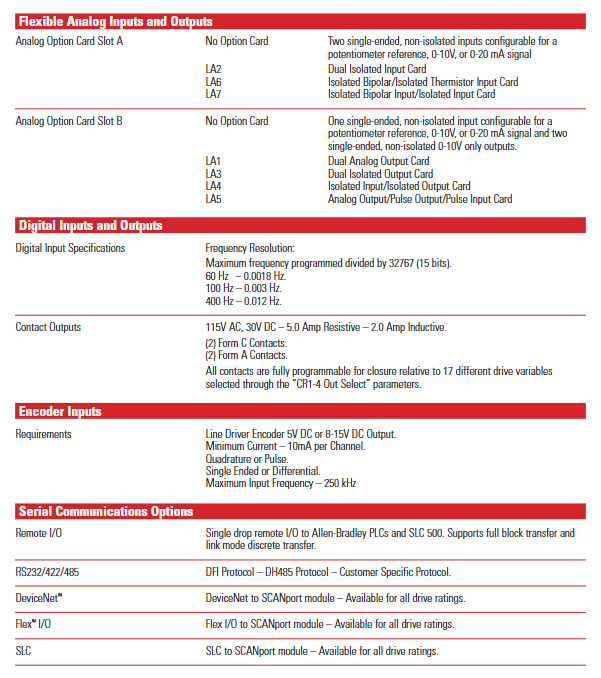
Analog I/O: Standard configuration supports 0-10V/0-20mA input (single ended non isolated), optional LA series isolation card (such as LA2 dual isolated input, LA3 dual isolated output), shielding layer needs to be connected to TE terminal.
The digital I/O: TB3 terminal supports 115V AC/24V AC/DC/TTL level input and can be programmed with functions such as start, stop, reverse, and preset speed selection; The output contacts (CR1-CR4) support 115V AC/30V DC, 5A resistive/2A inductive loads.
Encoder wiring: Supports 5V DC/8-15V DC line driven encoder (orthogonal or pulse signal), maximum input frequency 250kHz, single ended/differential signal can be used, and the shielding layer is connected to the TE terminal.
Selection and Configuration
1. Selection Guide
Model interpretation: The complete model format is "1336F-XXXXXX-XX", such as "1336F-B020-AA", where "B" represents the voltage/power code (460V, 20HP), "020" represents the power level, and "AA" represents the protection level (IP20/NEMA Type 1).
Load adaptation: The selection of constant torque (CT) and variable torque (VT) loads needs to be distinguished, for example, the 460V B020 model, CT rated 20HP, VT rated 25HP; the corresponding model needs to be selected according to the actual load type (such as CT for conveyor belt and VT for fan).
Option configuration: Supports factory pre installation or on-site installation options, such as communication cards (GM1 single node RIO, GM5 DeviceNet), control interface cards (L4 contact closed, L5 24V AC/DC), HIM (HA1 analog potentiometer, HJ2 digital potentiometer), braking units, reactors, etc.
2. Capacity reduction guide
When the operating conditions of the drive exceed the rated range, it is necessary to reduce the capacity. The core scenarios for reducing the capacity include:
Altitude: When it exceeds 1000m, the capacity decreases by about 6% for every 1000m increase (refer to Figure AD).
When the ambient temperature exceeds 40 ℃, the capacity will decrease by about 2% for every 1 ℃ increase (refer to Figure A-AC).
Carrier frequency: When it exceeds 4kHz (some models are 2kHz), the amplitude should be increased and the capacitance should be reduced according to the frequency (such as reducing the capacitance by 10% at 6kHz).
Fault handling and maintenance
1. Common faults and troubleshooting
The document lists more than 40 types of fault codes, and the core faults and their handling methods are as follows:
Fault code, fault name, cause analysis, and handling suggestions
04 Under voltage fault: Input voltage too low, bus capacitor fault, power failure. Check input voltage, replace capacitor, and confirm power stability
05 Overvoltage fault: Input voltage too high, brake unit fault, high load regeneration energy. Check input voltage, repair brake unit, and increase regeneration resistance
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- CTI
- Rolls-Royce
- General Electric
- Woodward
- Yaskawa
- xYCOM
- Motorola
- Siemens
- Rockwell
- ABB
- B&R
- HIMA
- Construction site
- electricity
- Automobile market
- PLC
- DCS
- Motor drivers
- VSD
- Implications
- cement
- CO2
- CEM
- methane
- Artificial intelligence
- Titanic
- Solar energy
- Hydrogen fuel cell
- Hydrogen and fuel cells
- Hydrogen and oxygen fuel cells
- tyre
- Chemical fiber
- dynamo
- corpuscle
- Pulp and paper
- printing
- fossil
- FANUC
- Food and beverage
- Life science
- Sewage treatment
- Personal care
- electricity
- boats
- infrastructure
- Automobile industry
- metallurgy
- Nuclear power generation
- Geothermal power generation
- Water and wastewater
- Infrastructure construction
- Mine hazard
- steel
- papermaking
- Natural gas industry
- Infrastructure construction
- Power and energy
- Rubber and plastic
- Renewable energy
- pharmacy
- mining
- Plastic industry
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- Wind energy
- International petroleum
- International new energy network
- gas
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- wind
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- YOKOGAWA
- TRICONEX
- FOXBORO
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- ADVANCED
- ALSTOM
- Control Wave
- AB
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- MOOG
- KB
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX


Email:wang@kongjiangauto.com