ABB IGCT Technology: A Revolutionary Breakthrough in High Voltage Inverters
To solve this dilemma, ABB Switzerland is exploring a new research and development path aimed at integrating the high-power advantages of IGBT with the core strengths of GTO, ultimately developing GCT (Gate Commutated Thyristor) and further developing it into IGCT, becoming an ideal alternative technology for GTO.
ABB IGCT Technology: A Revolutionary Breakthrough in High Voltage Inverters
Background and original intention of technology research and development
The development of power semiconductors has always been aimed at pursuing the "ideal switch", which requires the characteristics of low pass state and commutation loss, high commutation frequency, and simple driving circuit. In the low-voltage field, the technological iteration from transistors and Darlington transistors to IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) has achieved significant results. However, in the medium to high voltage field, the long-term dependence on GTO (Gate Turn Off Thyristor) poses problems such as complex control and limited performance.
To solve this dilemma, ABB Switzerland is exploring a new research and development path aimed at integrating the high-power advantages of IGBT with the core strengths of GTO, ultimately developing GCT (Gate Commutated Thyristor) and further developing it into IGCT, becoming an ideal alternative technology for GTO.
Principles and Breakthroughs of IGCT Core Technology
(1) Core improvement of GCT: solving GTO control problems
GTO has serious control issues and requires an unstable transition zone where both anode voltage and cathode current act simultaneously during shutdown, relying on buffer circuits for support. GCT breaks through this limitation through "hard drive" technology:
The rate of change of gate current reaches µ
(far exceeding GTO's 50 A/µ s), it can switch the current from the cathode to the gate before there is a significant change in the charge distribution between the gate and anode.
Directly switch the device from thyristor mode to transistor mode, with stable and fast turn off process, no need for buffer circuit, and performance close to IGBT.
(2) The Four Key Development Steps of IGCT Converter
Low inductance drive design
To avoid the GCT entering the unstable working zone, the cathode current needs to be turned off within 1 µ s, and the leakage inductance of the gate circuit corresponding to the 3kA GCT should be ≤ 6nH (only 1/50 of the conventional value of GTO).
Low inductance is achieved through a multi-layer connection between the coaxial device connection structure and the driving power output, while using a gate voltage of -20V to balance reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Optimize silicon wafer technology
Hard drive technology allows GCT silicon wafers to be designed thinner without compromising on switch characteristics, combined with plasma engineering technology, significantly reducing losses (compared to GTO of the same specification, the commutation loss is similar but the on state loss is lower).
High integration and linear scaling of current
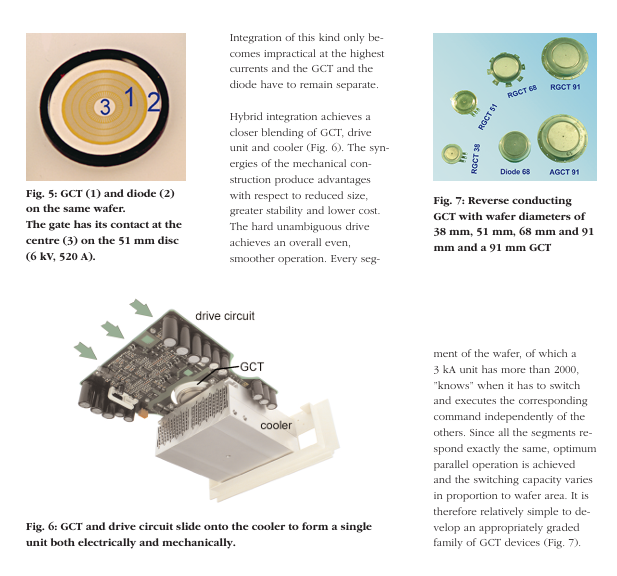
Integration is divided into two levels: one is single-chip integration (integrating anti parallel diodes and GCTs on the same silicon wafer to reduce diode stacking and high current connections); The second is hybrid integration (integrating GCT, driving unit, and cooler to reduce volume, improve stability, and lower costs).
Each unit of the silicon wafer (3kA devices containing over 2000 units) synchronously responds to switch instructions, achieving optimal parallel operation. The current capacity is linearly related to the silicon wafer area, making it easy to develop multi specification GCT series (such as devices with silicon wafer diameters of 38mm, 51mm, 68mm, and 91mm).
Simplify circuit complexity
No buffering capacitors, diodes, and resistors are required for GTO converters, only the current rise rate when GCT is turned on needs to be limited (as high-voltage silicon diodes are slower than low-voltage IGBT diodes).
By adopting a new high current circuit, all phases of the inverter can be connected to the same DC bus, which is comparable in cost to conventional IGBT converters.
(3) Modular design and high-voltage adaptation
Modular component system: In response to the diverse application requirements and small batch size of high-power converters, IGCT adopts modular design, which can cover a power range of 250kW to 100MW through unit series connection and adapt to different scenarios.
Pressure contact technology: Traditional module technology is difficult to handle high voltage and high current. IGCT adopts an improved pressure contact technology, which integrates the driving unit, power semiconductor, and cooler into a single functional unit. It replaces expensive chip parallel arrays with optimized silicon wafers in standard packaging, simplifies manufacturing, reduces costs, and is easy to maintain.
Performance advantages and application cases of IGCT converters
(1) Core performance advantages
Category specific advantages
Component characteristics include high rated voltage, low turn-on and commutation losses, high commutation frequency (intermittent up to 7kHz, average 500Hz for three-point converters, equivalent two-point 2kHz), high silicon wafer utilization, uniform current distribution, linear correlation between current capacity and silicon wafer area, and easy modeling
Circuit design includes a three-phase shared DC bus, a central dI/dt limiter with integrated clamping, simple intermediate circuit connection, safety and reliability under extreme working conditions, and a simple driving circuit (directly coupled with switch signals, no dV/dt or dI/dt regulation circuit required, dual line low-power power supply)
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA




































































































































