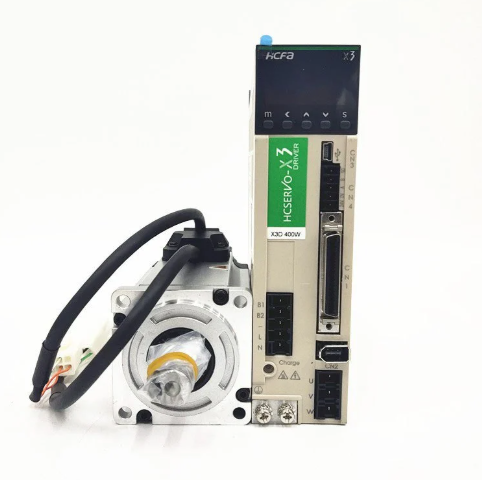
ABB Sace BSD series brushless servo drive
BSD0750 BSM0750xxxx 750W 3000r/min
BSD1000 BSM1000xxxx 1000W 2000r/min
BSD1500 BSM1500xxxx 1500W 2000r/min
BSD2000 BSM2000xxxx 2000W 2000r/min
(Note: "xxxx" represents motor shaft type, brake and options, such as BSM0100CN00=100W, keyway shaft, no brake, no options)
Differences in power wiring:
0.4kW and below (BSD0100/0200/0400): Only supports single-phase 200-230VAC, wired to L1 and L2 terminals, voltage fluctuation allowed -10%~+10%.
0.75kW (BSD0750): Supports single-phase or three-phase 200-230VAC, with single-phase connected to L1 and L2, and three-phase connected to L1, L2, and L3; Single phase voltage fluctuation -10%~+10%, three-phase -15%~+10%.
0.85kW and above (BSD1000/1500/2000): Only supports three-phase 200-230VAC, wired to terminals L1, L2, and L3, with allowable voltage fluctuations of -15% to+10%.
All models of control power supply are unified as single-phase 200-230VAC, wired to sL1 and sL2 terminals, with voltage fluctuations ranging from -10% to+10%.
Question 2: What are the core objectives and key operational steps of the three-stage testing in the testing operation of BSD series servo systems? What are the requirements to pay attention to when returning to the origin?
Answer:
Core purpose and steps of three-stage testing:
Key operational steps for the core objectives of the stage
In the first stage, verify that the servo amplifier and motor work separately and eliminate basic wiring/hardware faults. 1. Fix the motor (axis without load); 2. Connect the amplifier motor power/encoder cable (not connected to CN1); 3. Power on and check the charging LED and keyboard display; 4. Test the rotation direction of the motor (parameter # 04) and ensure there are no alarms
The communication and command response between the second stage verification and the upper control system are normal. 1. Connect amplifier CN1 to the upper system; 2. Check the I/O signals (emergency stop EMG, overtravel ± OT, brake timing); 3. Power on and output pulse/analog commands, check motor speed, rotation direction, and I/O signal recognition
The third stage verifies that the motor operates normally as a whole after installation and meets the actual working conditions. 1. Securely install the motor onto the machine; 2. Reproduce the second stage I/O signal inspection; 3. Verify that the machine travel matches the instructions; 4. Adjust servo parameters (refer to Chapter 6) to ensure positioning accuracy/no vibration
Origin regression requirements:
After power failure and restart, the motor needs to rotate 372 ° or more at a speed of * * ≤ 100r/min (approximately 1.04 revolutions, motor output shaft angle) in order to correctly detect the encoder Z phase.
If the requirements of "speed ≤ 100r/min+rotation ≥ 372 °" are not met, the Z-phase cannot be correctly identified, which may result in the motor rotating an additional circle after returning to the origin.
Question 3: In the BSD series servo system, what scenarios are the three settings (automatic/semi-automatic/manual) of core parameter # 05 (tuning mode) applicable to? How to suppress mechanical vibration through parameter adjustment?
Answer:
Tuning mode (parameter # 05) Applicable scenarios:
Tuning mode parameter # 05 setting applicable scenario operation points
Automatic tuning: Most conventional mechanical amplifiers (with stable load inertia and no special resonance) automatically estimate the load inertia ratio without manually setting # 06, directly generating the optimal gain (such as # 40/# 41/# 42)
Semi automatic tuning 1. Inaccurate load inertia estimation scenarios (such as large load fluctuations, high friction, and applications with thrust) 1. Manually set # 06 (load inertia ratio, read or calculated through keyboard monitoring mode); 2. The amplifier automatically calculates gain based on # 06
Manual tuning 2 automatic/semi-automatic tuning failure scenarios (such as obvious mechanical resonance and high rigidity requirements) 1. Manually set # 40 (position controller gain), # 41 (velocity response), and # 42 (velocity integration time); 2. Optimize with # 45 (feedforward filtering) and # 46 (torque filtering); 3. Use BSD Configurator to monitor waveforms
Parameter adjustment method for suppressing mechanical vibration:
Method 1: Enable vibration suppression control (position control only):
First, optimize the servo gain according to Chapter 6 "Basic Adjustment" (ensuring no basic vibration);
Find the mechanical anti resonance frequency (5.0-200.0Hz) through the BSD Configurator servo analysis function;
Set the anti resonance frequency to parameter # 60- # 63 (anti resonance frequency 0-3), while setting # 43 (S-curve time constant, reference: anti resonance frequency<10Hz set 10ms, 10-20Hz set 5ms,>20Hz set 2-3ms).
Method 2: Use notch filter (position/velocity control):
Find the mechanical resonance frequency (through servo analysis function);
Set parameter # 56 (notch filter 1 frequency)=resonance frequency, # 57 (notch filter 1 damping)=5-20dB (to avoid excessive control instability);
If there are two resonance points, repeat step 2 to set # 58 (filter 2 frequency) and # 59 (filter 2 damping).
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- CTI
- Rolls-Royce
- General Electric
- Woodward
- Yaskawa
- xYCOM
- Motorola
- Siemens
- Rockwell
- ABB
- B&R
- HIMA
- Construction site
- electricity
- Automobile market
- PLC
- DCS
- Motor drivers
- VSD
- Implications
- cement
- CO2
- CEM
- methane
- Artificial intelligence
- Titanic
- Solar energy
- Hydrogen fuel cell
- Hydrogen and fuel cells
- Hydrogen and oxygen fuel cells
- tyre
- Chemical fiber
- dynamo
- corpuscle
- Pulp and paper
- printing
- fossil
- FANUC
- Food and beverage
- Life science
- Sewage treatment
- Personal care
- electricity
- boats
- infrastructure
- Automobile industry
- metallurgy
- Nuclear power generation
- Geothermal power generation
- Water and wastewater
- Infrastructure construction
- Mine hazard
- steel
- papermaking
- Natural gas industry
- Infrastructure construction
- Power and energy
- Rubber and plastic
- Renewable energy
- pharmacy
- mining
- Plastic industry
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- Wind energy
- International petroleum
- International new energy network
- gas
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- wind
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- YOKOGAWA
- TRICONEX
- FOXBORO
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- ADVANCED
- ALSTOM
- Control Wave
- AB
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- MOOG
- KB
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX
- BENDER
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN


Email:wang@kongjiangauto.com